A deeply eroded giant volcano, active from ancient through recent times and with possible remnants of glacier ice near its base, had been hiding near Mars’ equator in plain sight. Its discovery points to an exciting new place to search for life, and a potential destination for future robotic and human exploration.
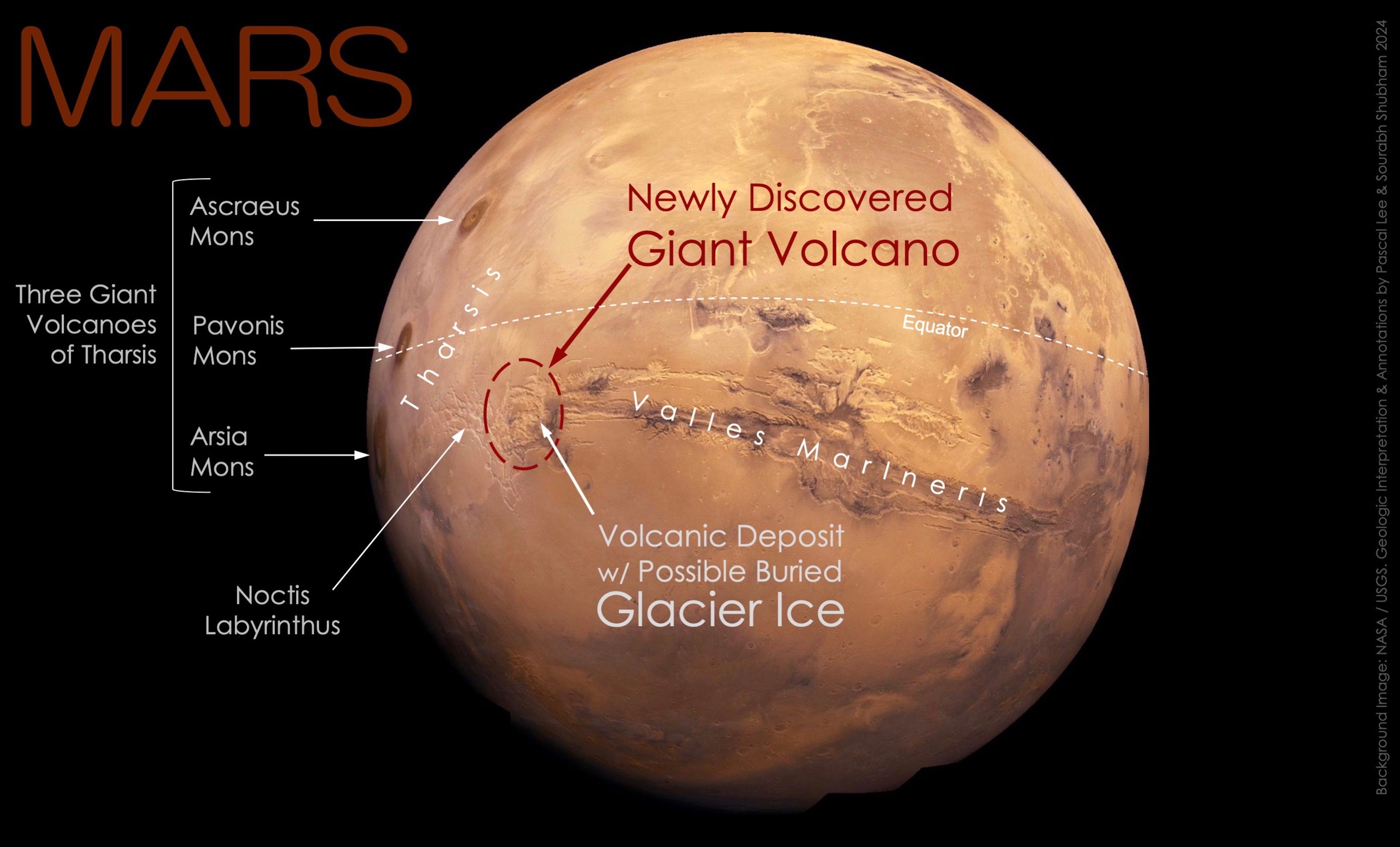
The newly discovered giant volcano on Mars is located just south of the planet’s equator, in Eastern Noctis Labyrinthus, west of Valles Marineris, the planet’s vast canyon system. The volcano sits on the eastern edge of a broad regional topographic rise called Tharsis, home to three other well-known giant volcanoes: Ascraeus Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Arsia Mons. Although more eroded and less high than these giants, the newly discovered volcano rivals the others in diameter, which is about 450 km (280 miles) (red dashed circle in this picture). Possible buried glacier ice is also reported under a relatively recent volcanic deposit within the perimeter of the eroded volcano, making the area attractive for the search for life and future robotic and human exploration. (Credit: Background image: NASA/USGS Mars globe. Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024).
March 13, 2024, Mountain View, California – In a groundbreaking announcement at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference held in The Woodlands, Texas, scientists revealed the discovery of a giant volcano and possible sheet of buried glacier ice in the eastern part of Mars’ Tharsis volcanic province, near the planet’s equator. Imaged repeatedly by orbiting spacecraft around Mars since Mariner 9 in 1971 - but deeply eroded beyond easy recognition, the giant volcano had been hiding in plain sight for decades in one of Mars’ most iconic regions, at the boundary between the heavily fractured maze-like Noctis Labyrinthus (Labyrinth of the Night) and the monumental canyons of Valles Marineris (Valleys of Mariner) (Fig. 1).
Provisionally designated “Noctis volcano” pending an official name, the structure is centered at 7° 35' S, 93° 55' W. It reaches +9022 meters (29,600 feet) in elevation and spans 450 kilometers (280 miles) in width. The volcano’s gigantic size and complex modification history indicate that it has been active for a very long time. In its southeastern part lies a thin, recent volcanic deposit beneath which glacier ice is likely still present. This combined giant volcano and possible glacier ice discovery is significant, as it points to an exciting new location to study Mars’ geologic evolution through time, search for life, and explore with robots and humans in the future (Fig.2).

“We were examining the geology of an area where we had found the remains of a glacier last year when we realized we were inside a huge and deeply eroded volcano,” said Dr. Pascal Lee, planetary scientist with the SETI Institute and the Mars Institute based at NASA Ames Research Center, and the lead author of the study.
Several clues, taken together, give away the volcanic nature of the jumble of layered mesas and canyons in this eastern part of Noctis Labyrinthus. The central summit area is marked by several elevated mesas forming an arc, reaching a regional high and sloping downhill away from the summit area. The gentle outer slopes extend out to 225 kilometers (140 miles) away in different directions. A caldera remnant – the remains of a collapsed volcanic crater once host to a lava lake – can be seen near the center of the structure. Lava flows, pyroclastic deposits (made of volcanic particulate materials such as ash, cinders, pumice and tephra) and hydrated mineral deposits occur in several areas within the structure’s perimeter (Figs. 3, 4 and 5).
“This area of Mars is known to have a wide variety of hydrated minerals spanning a long stretch of Martian history. A volcanic setting for these minerals had long been suspected. So, it may not be too surprising to find a volcano here,” explained Sourabh Shubham, a graduate student at the University of Maryland’s Department of Geology and the study’s co-author. “In some sense, this large volcano is a long-sought ‘smoking gun’”.
In addition to the volcano, the study reports the discovery of a large, 5000 square kilometer (1930 square mile) area of volcanic deposits within the volcano’s perimeter presenting a large number of low, rounded and elongated, blister-like mounds. This “blistered terrain” is interpreted to be a field of “rootless cones,” mounds produced by explosive steam venting or steam swelling when a thin blanket of hot volcanic materials comes to rest on top of a water or ice-rich surface (Figs. 3 and 6).
Just a year ago, Lee, Shubham and their colleague John W. Schutt had identified the spectacular remains of a glacier - or “relict glacier” - through a sizeable erosional opening in the same volcanic blanket, in the form of a light-toned deposit (LTD) of sulfate salt with the morphologic traits of a glacier. The sulfate deposit, made mainly of jarosite, a hydrous sulfate, was interpreted to have formed when the blanket of volcanic pyroclastic materials came to rest on a glacier and reacted chemically with the ice. Breached rootless cones identified in the current study show similar occurrences of polyhydrated sulfates, further suggesting the blistered volcanic blanket may be hiding a vast sheet of glacier ice underneath it (Fig. 6).

The Noctis volcano does not present the conventional cone shape of a typical volcano because a long history of deep fracturing and erosion has modified it. However, upon close inspection, key features indicative of a volcano are recognizable. Within the “inner zone” delineating the highest elevation remains of the volcano, an arc of high mesas marks the central summit area, culminating at +9022 m (29,600 ft). Preserved portions of the volcano’s flanks extend downhill in different directions to the outer edge of the “outer zone,” 225 km (140 miles) away from the summit area. A caldera remnant – the remains of a collapsed volcanic crater once host to a lava lake – can be seen near the center of the structure. Lava flows, pyroclastic deposits (made of volcanic particulate materials such as ash, cinders, pumice and tephra) and hydrothermal mineral deposits occur in several areas within the perimeter of the volcanic structure. The map also shows the rootless cone field and possible extent of shallow buried glacier ice reported in this study, in relation to the “relict glacier” discovered in 2023. Noctis Landing, a candidate landing site for future robotic and human exploration, is also shown. (Credit: Background images: NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Context Camera (CTX) mosaic and Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) digital elevation model. Geologic interpretation & annotations by Pascal Lee & Sourabh Shubham 2024).

Detailed analysis of the altimetry of the region using NASA’s Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data, in combination with high resolution imaging data from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) and Context Imager (CTX), and from the European Space Agency’s Mars Express (MEX) High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) enabled the discovery of the Noctis volcano. In addition to the volcano’s summit, caldera remnant, and inner and outer zones, the topographic map on the right shows the “relict glacier” discovered in 2023 and Noctis Landing, a candidate landing site for future robotic and human exploration. (Credit: Left: Mars Express HRSC color mosaic © ESA/DLR/FU Berlin CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO; Right: Background image: same as Left; NASA MGS MOLA digital elevation model. Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024).

Anaglyph image showing portions of the Noctis volcano’s 250 km (155 mile) diameter inner zone of high elevation remains, and 450 km (280 mile) diameter outer zone of other remains associated with the volcano. In addition to the volcano’s summit, caldera remnant, and inner and outer zones, this 3D map shows the “relict glacier” discovered in 2023 and Noctis Landing, a candidate landing site for future robotic and human exploration. (Credit: Background image: Mars Express anaglyph (3D) mosaic © ESA/DLR/FU Berlin CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024).

A well-preserved volcanic lava flow and pyroclastic deposit in the southeastern part of the Noctis volcano suggest that the volcano remained active even in relatively recent times. The pyroclastic deposit presents “blisters” at its surface, interpreted as “rootless cones” or steam vents produced when the hot pyroclastic materials came in contact with H2O ice. Breaches in the pyroclastic deposit reveal light-toned deposits (LTDs) of sulfate salts, expected products of chemical reactions between pyroclastic materials and H2O ice. The largest LTD of sulfates in this area had already been described as a “relict glacier,” as it presents a wide range of morphologic traits specific to glaciers, suggesting that glacier ice might still be preserved, only protected under a thin layer of sulfate salts. By extension, the rootless cones and other sulfate deposits in this area may be blanketing even more glacier ice. (Credit: Background images: NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), Context Imager (CTX), and Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM). Geologic interpretation and annotations by Pascal Lee and Sourabh Shubham 2024).
The Noctis volcano presents a long and complex history of modification, possibly from a combination of fracturing, thermal erosion, and glacial erosion. Researchers interpret the volcano to be a vast shield made of layered accumulations of pyroclastic materials, lavas, and ice, the latter resulting from repeated buildups of snow and glaciers on its flanks through time. As fractures and faults eventually developed, in particular in connection with the uplift of the broader Tharsis region on which the volcano sits, lavas began to rise through different parts of the volcano, leading to thermal erosion and removal of vast amounts of buried ice and the catastrophic collapse of entire sections of the volcano.
Subsequent glaciations continued their erosion, giving many canyons within the structure their present distinctive shape. In this context the “relict glacier” and the possible buried sheet of glacier ice around it, might be remnants of the latest glaciation episode affecting the Noctis volcano.
But much about the newly discovered giant volcano remains a mystery. Although it is clear that it has been active for a long time and began to build up early in Mars’ history, it is unknown how early exactly. Similarly, although it has experienced eruptions even in modern times, it is unknown if it is still volcanically active and might erupt again. And if it has been active for a very long time, could the combination of sustained warmth and water from ice have allowed the site to harbor life?
As mysteries surrounding the Noctis volcano continue to puzzle scientists, the site is already emerging as an exciting new location to study Mars’ geologic evolution, search for life, and plan future robotic and human exploration. The possible presence of glacier ice at shallow depths near the equator means that humans could potentially explore a less frigid part of the planet while still being able to extract water for hydration and manufacturing rocket fuel (by breaking down H2O into hydrogen and oxygen).
“It’s really a combination of things that makes the Noctis volcano site exceptionally exciting. It’s an ancient and long-lived volcano so deeply eroded that you could hike, drive, or fly through it to examine, sample, and date different parts of its interior to study Mars’ evolution through time. It has also had a long history of heat interacting with water and ice, which makes it a prime location for astrobiology and our search for signs of life. Finally, with glacier ice likely still preserved near the surface in a relatively warm equatorial region on Mars, the place is looking very attractive for robotic and human exploration,” said Lee.
This study was conducted using data from NASA’s Mariner 9, Viking Orbiter 1 and 2, Mars Global Surveyor, Mars Odyssey, and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter missions, as well as ESA’s Mars Express mission. Special appreciation is expressed to their instrument teams for acquiring the various datasets used in this study. Use of the open NASA Planetary Data System, Mars Quickmap, Mars Trek, and Google Mars online data visualization tools was also key in enabling the study.
About the SETI Institute
Founded in 1984, the SETI Institute is a non-profit, multidisciplinary research and education organization whose mission is to lead humanity’s quest to understand the origins and prevalence of life and intelligence in the universe and share that knowledge with the world. Research at the SETI Institute encompasses the physical and biological sciences and leverages expertise in data analytics, machine learning and advanced signal detection technologies. The SETI Institute is a distinguished research partner for industry, academia and government agencies, including NASA and NSF.
About Mars Institute
The Mars Institute is a non-profit research organization dedicated to the advancement of Mars science, exploration, and the public understanding of Mars. Research at the Mars Institute focuses Mars and other planetary destinations that may serve as stepping-stones to Mars, in particular Mars’ moons, our Moon, and near-Earth objects. The Mars Institute investigates the technologies and strategies that will enable and optimize the future human exploration of Mars. The Mars Institute operates the Haughton-Mars Project Research Station on Devon Island, High Arctic.
For more information, contact:
Rebecca McDonald
Director of Communications
SETI Institute
339 Bernardo Ave, Suite 200
Mountain View, CA 94043
USA
E-mail: rmcdonald@seti.org
Dr Pascal Lee
Planetary Scientist
SETI Institute & Mars Institute
NASA Ames Research Center
MS 245-3
Moffett Field, CA 94035-1000
USA
E-mail: pascal.lee@marsinstitute.net





